4 Weeks Pregnant With Twins: Twin Pregnancy Symptoms
At 4 weeks pregnant with twins you may not feel any changes in your body yet, but that doesn’t mean that nothing is going on. Your babies are like two tiny balls – called blastocysts – and are already consisting of several hundred cells that are multiplying.
In this article
- Pregnancy test at 4 weeks
- Twin pregnancy symptoms at 4 weeks
- Baby size & development at 4 weeks
- How identical and fraternal twins develop
- 4 weeks pregnant with twins belly
- 4 weeks pregnant with twins ultrasound
- Twin pregnancy diet
- Gestational diabetes in twin pregnancy
- What you need to buy
What you need to buy
There’s not much you need to buy yet, but taking a folic acid supplement is crucial. Ideally, you should begin taking folic acid at least a month prior to you getting pregnant, and it’s very important that you start immediately, if you haven’t. Folic acid is a B vitamin and it’s standard for pregnant women and women who plan to become pregnant. Folic acid helps prevent neural tube defects. Neural tube defects are serious birth defects of the spinal cord and the brain. You need to take folic acid for the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. There are folic acid in prenatal multivitamin tablets as well.
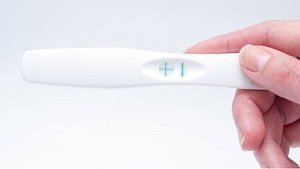
Pregnancy test at 4 weeks
You may be able to get a positive pregnancy test result, when you’re 4 weeks pregnant with twins, but don’t count on it. You can buy pregnancy tests that promise early results up to six days sooner than your missed period. However, the longer you wait, the more conclusive the test result will be. The levels of the pregnancy hormone hCG need to be high enough to be detected by pregnancy tests. The pregnancy hormone tells your ovaries to stop releasing eggs. It also triggers increased production of estrogen and progesterone. These hormones keep your uterus from shedding its lining and stimulate the growth of the placenta(s). You won’t ovulate while you’re pregnant.* This also means that you won’t get your period.
*It’s possible for a woman to continue ovulating after becoming pregnant, but it’s very rare. It’s called superfetation if a woman becomes pregnant while already pregnant. Read more about it in different types of twins.
Twin pregnancy symptoms at 4 weeks
- Some women might notice spotting – or slight bleeding – for one or two days around the time of implantation. This is called implantation bleeding. It happens when the fertilized eggs attach to the inside of the uterus. After implantation, the lining of the uterus gets thicker, and the cervix is sealed by a plug of mucus. It will stay in place until the twins are ready to be born.
- Some women report feeling nauseous very early on when they are pregnant with twins. This is probably due to the hormonal changes you’re experiencing.
- Some women experience cramps similar to when you’re getting your period. It’s not necessarily a bad sign. Wait a couple of days to see if you get your period and, if not, take a pregnancy test.
Baby size and development at 4 weeks
Your babies (or baby)* are like two tiny balls – called blastocysts – and are already consisting of several hundred cells that are multiplying. The part that will develop into the placenta(s) has started producing the pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). The blastocysts are receiving oxygen and nutrients from their yolk sac(s) until the placenta(s) is ready to take over.
*If you’re having identical twins, the egg may not have split yet.
When you’re 4 weeks pregnant with twins, the fertilized eggs reach your uterus. With fraternal twins, two eggs have been released from your ovaries and have fertilized by two separate sperm cells. Identical twins stem from an egg splitting in two after fertilization. The eggs will now attach to the lining of your uterus. This is called implantation.
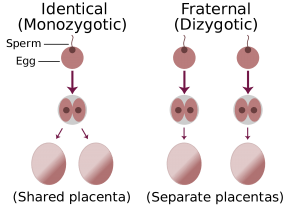
How identical & fraternal twins develop
Fraternal twins have their own separate placentas, amniotic sac and outer membrane. If an egg splits within the first three days after ovulation, identical twins will have their own placenta, amniotic sac and outer membrane similar to fraternal twins. This type of twin pregnancy is called a dichorionic-diamniotic (di-di) twin pregnancy. If the split happens later, the twins will share an outer membrane and placenta. In most cases, they each have their own separate, inner membrane. This is the case for two thirds of identical twins, so it’s the most common type of identical twin. This is called a monochorionic-diamniotic (mo-di) twin pregnancy. It’s possible for identical twins to share an inner membrane (amniotic sac) too, but it’s very rare and only happens in about one percent of identical twin pregnancies. This is called a monochorionic-monoamniotic (mo-mo) twin pregnancy. Twins who share a placenta are more at risk of twin pregnancy complications, so it’s very important to get a chorionicity scan early on.
4 weeks pregnant with twins belly
Your babies aren’t big enough for you to be showing at 4 weeks pregnant with twins. If you belly looks or feels a little bit larger than usually it’s probably due to blowing relating to the hormonal changes. Have a look at week by week twin pregnancy belly pictures from a lot of different twin pregnancies.
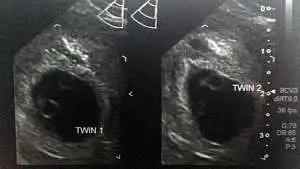
4 weeks pregnant with twins ultrasound
When you’re 4 weeks pregnant with twins, you won’t be able to detect the pregnancy by the use of ultrasound. When six full weeks have passed (after week 6+0) you should be able to detect all kinds of twins using ultrasound. The ultrasound picture above is of identical twins who share a placenta at 6+2 weeks. Read more about twin ultrasound and what you need to pay attention to.
Twin pregnancy diet
Eating healthy, nutritious food is important for you and your babies during pregnancy. You especially need to make sure that you get enough protein and calcium. You can get calcium and protein through dairy products, eggs, lean meat, lentils, peas, beans, chickpeas, soybeans, peanuts and vegetables such as kale and spinach. It’s very important that you cut down on sugar. Both in terms of candy and sugary drinks but also ready meals with added sugar. You increase the risk of getting gestational diabetes if you eat foods that are high in sugar.
Gestational diabetes in twin pregnancy
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. It can not only affect your health but also the health of your babies. It makes you and your babies more at risk for type 2 diabetes, and your babies are more likely to be born too large. This makes them at risk of sustaining birth injuries or require a c-section delivery. They are also more at risk of being born prematurely, having low blood sugar and trouble breathing. You will be at risk of high blood pressure and preeclampsia. Luckily there are steps you can take to prevent or control gestational diabetes and reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Eating healthy foods and exercising can help reduce the risk of future type 2 diabetes. Of those women with a history of gestational diabetes who reach their ideal body weight after delivery, fewer than 1 in 4 eventually develop type 2 diabetes.